
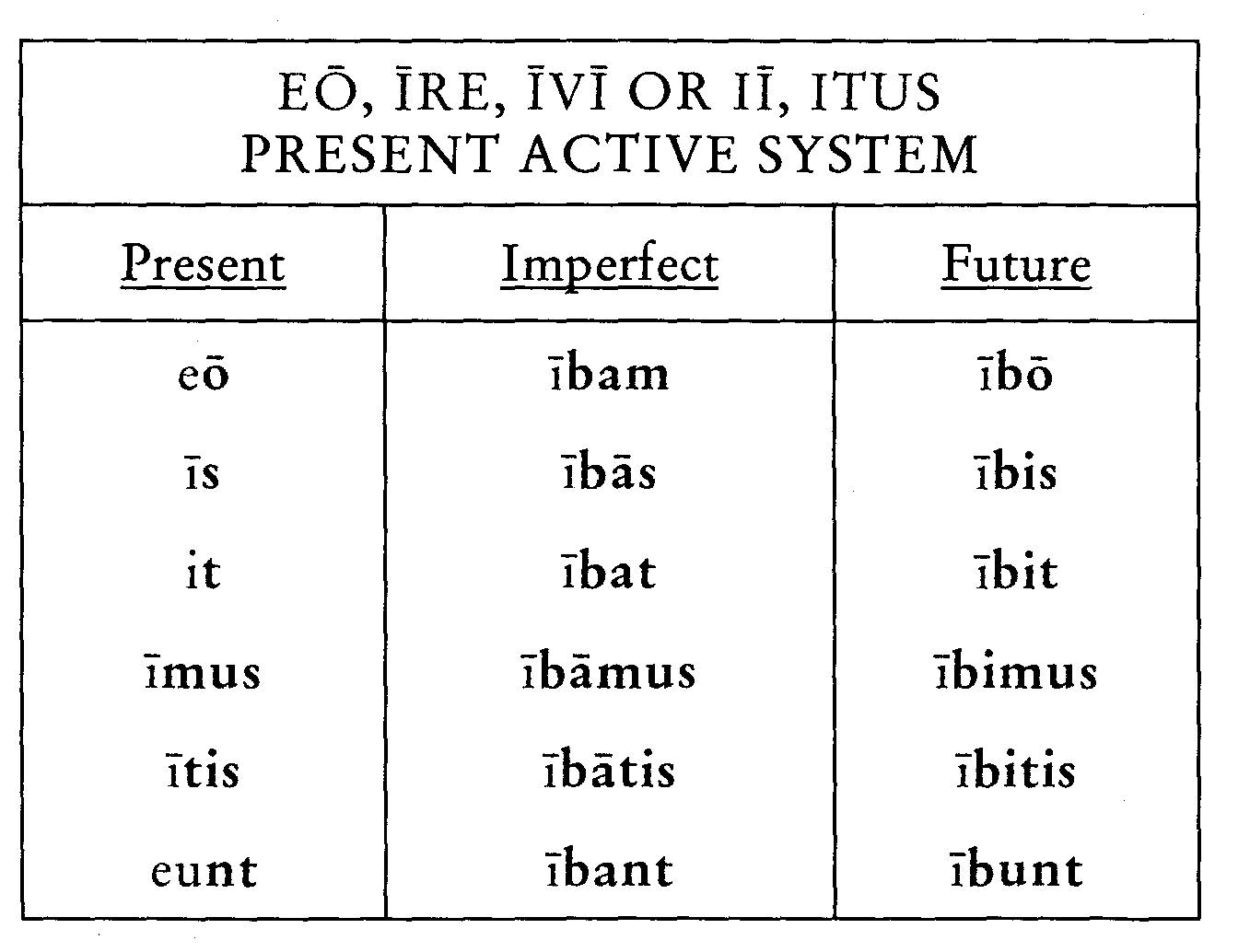
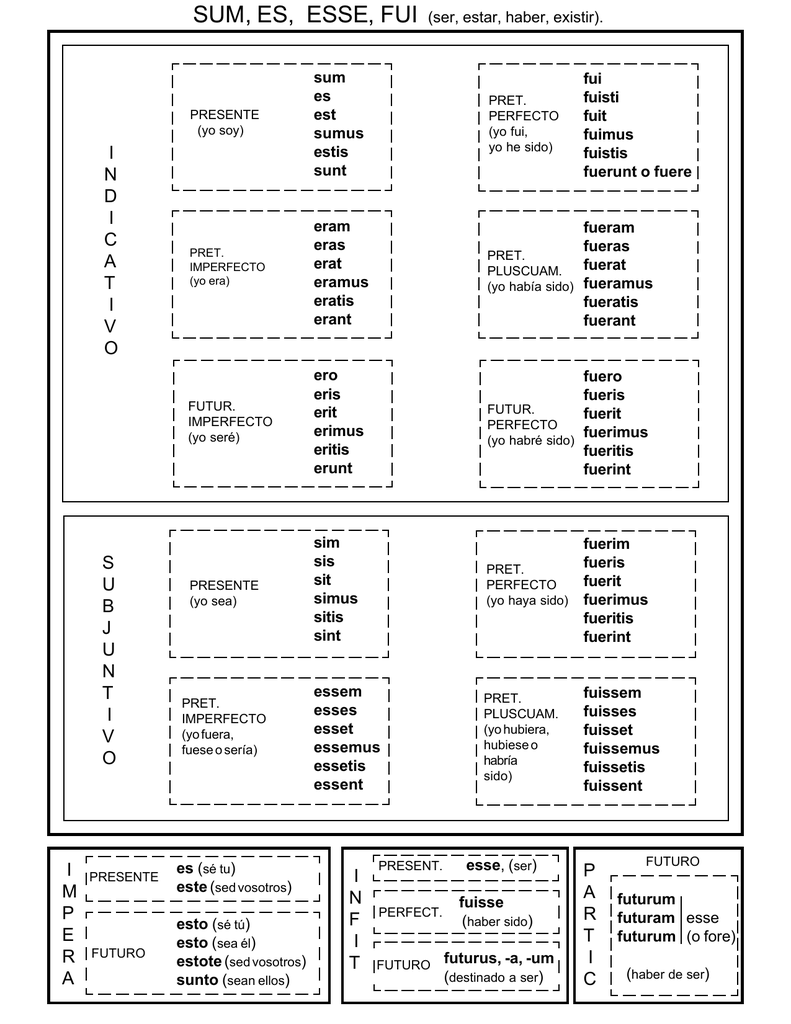
There are two forms of the perfectum tenses. The perfect tenses are made using the perfect participle of the verb together with part of the verb sum 'I am'. Passive and deponent verbs are constructed as follows. The verb sum 'I am' is exceptional, since it has a future infinitive fore, which makes an additional subjunctive, forem (described below): Shortened forms, such as amāsse and amāssem, are frequently found. Other verbs, such as amō 'I love', form the future in a different way: In verbs such as dūcō, the future indicative and present subjunctive are the same in the 1st person singular ( dūcam), but differ in the other persons. To these must be added three participles, present participle ( dūcēns), future participle ( ductūrus), and perfect participle ( ductus), a gerundive ( dūcendus), and two imperative tenses, present ( dūc!) and future ( dūcitō!). Substituting the verb dūcō 'I lead' in the table gives the following forms: The infectum tenses usually refer to events which are or were in progress, or which have not yet happened, while perfectum tenses describe events which have happened already or which will have happened at some future time. The main Latin tenses can be put in a table as follows: Main Latin tenses In some cases Latin makes a distinction which is not made in English: for example, imperfect eram and perfect fuī both mean 'I was' in English, but they differ in Latin. Latin tenses do not have exact English equivalents, so that often the same tense can be translated in different ways depending on its context: for example, dūcō can be translated as 'I lead', 'I am leading' or 'I led', and dūxī can be translated as 'I led' and 'I have led'. The infinitive has two main tenses (present and perfect) as well as a number of periphrastic tenses used in reported speech. Participles in Latin have three tenses (present, perfect, and future). In addition to these six tenses of the indicative mood, there are four tenses in the subjunctive mood and two in the imperative mood. However, these are less commonly used than the six basic tenses. To these six main tenses can be added various periphrastic or compound tenses, such as ductūrus sum 'I am going to lead', or ductum habeō 'I have led'. The main Latin tenses can be divided into two groups: the present system (also known as infectum tenses), consisting of the present, future, and imperfect and the perfect system (also known as perfectum tenses), consisting of the perfect, future perfect, and pluperfect. For Latin tenses from a functional perspective, see Latin tenses (semantics).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
